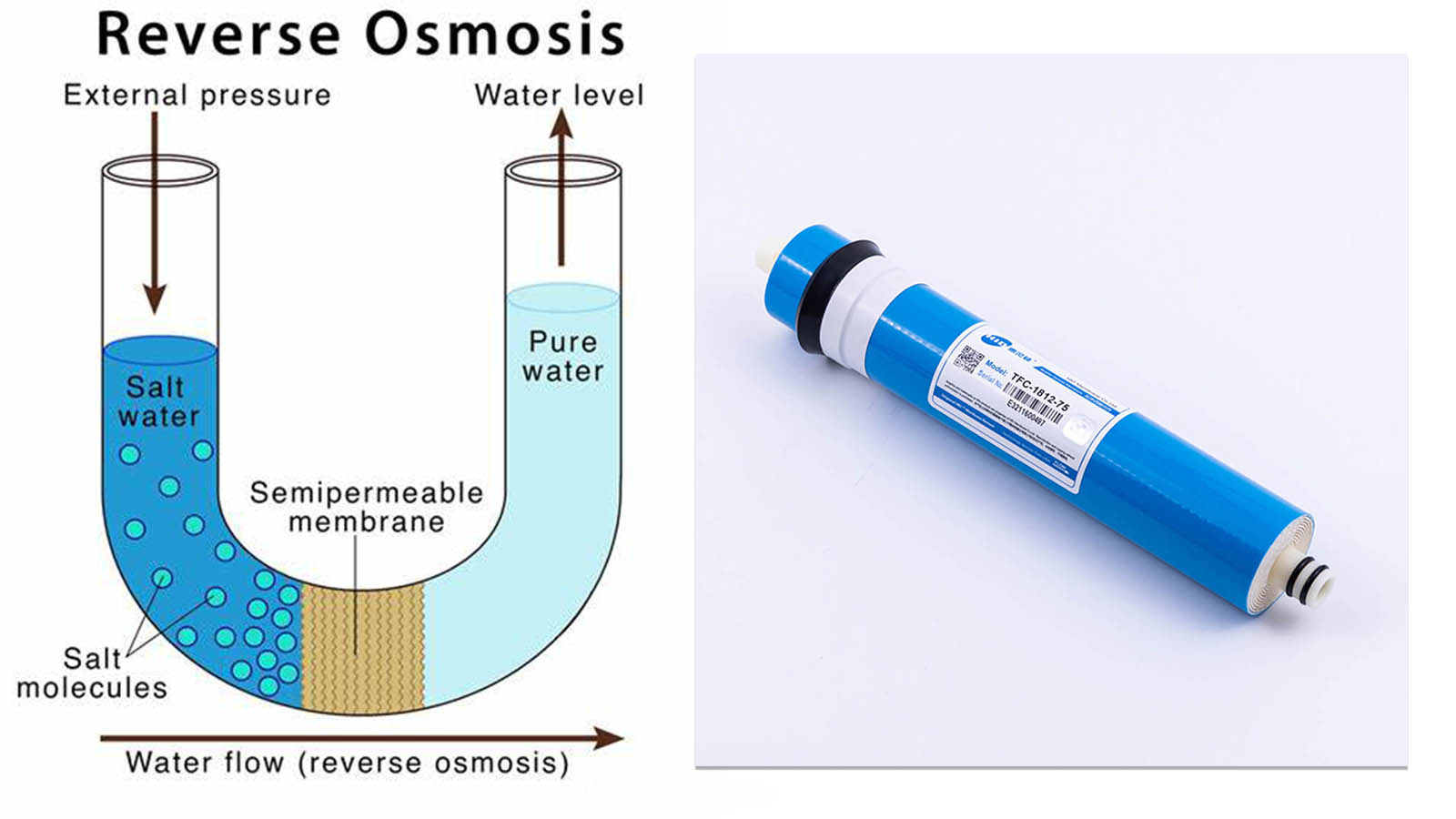
This is a diagram outlining the process of Reverse Osmosis. When pressure is applied to the concentrated solution, the water molecules are forced through the semi-permeable membrane and the contaminants are not allowed through.
The reverse osmosis membrane then removes molecules heavier than water, such as sodium, high levels of lead, dissolved minerals, and fluoride. Finally, the post-carbon filter polishes the water.